In this article
- What is alopecia areata?
- What are the signs of alopecia areata?
- What causes alopecia areata?
- Circular hair loss - frequency and age
- Alopecia areata symptoms
- Prognosis: How does circular hair loss progress?
- Alopecia areata self-care
- Therapy: Alopecia areata treatments and alopecia areata medication
- The last words
Alopecia areata, a condition causing bald patches on the scalp, perplexes experts due to its elusive cause. This form of hair loss, termed "circular hair loss," presents challenges in treatment. The mysterious nature of its origins makes finding effective solutions challenging.
Individuals affected by this condition often face not only physical changes but also emotional struggles. Understanding alopecia areata is crucial in providing support and developing treatments to alleviate its impact on those affected. In the following, you can review what causes this hair problem and learn how to avoid it properly.
What is alopecia areata?
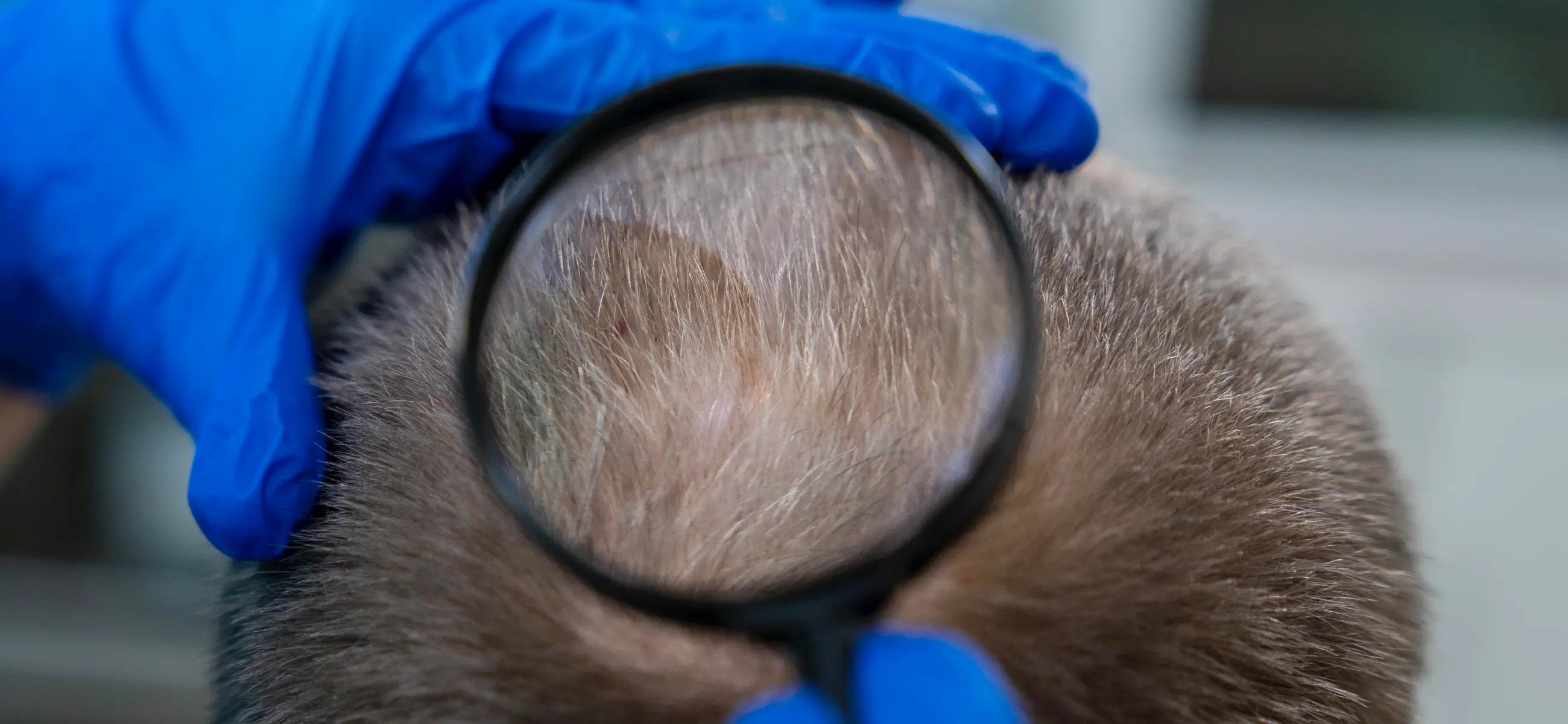
Circular hair loss usually results in a hairless patch on the scalp with a diameter of 1-2 centimeters. This is often followed by other bald patches. The affected patches are not always exactly circular or round but are clearly demarcated from their hairy surroundings. Alopecia areata does not cause pain but may be accompanied by slight itching.
What are the signs of alopecia areata?
The first signs of circular hair loss (alopecia areata) usually appear unexpectedly: All of a sudden, round, hairless patches appear where hair was previously present.
In most sufferers, only the hair on the head is affected. In rare cases, however, eyebrows, eyelashes, beard, or other hairy parts of the body can also be affected by hair loss.
In most cases, only individual hairless "islands" form with circular hair loss. However, there are also fewer common subtypes with a different appearance:
-
In alopecia areata totalis, the hairless patches flow into one another until the entire head is bald.
-
In alopecia areata universalis, the entire body is affected by hair loss.
-
In ophiasis-type alopecia areata, the hair on the nape or back of the head disappears.
What causes alopecia areata?
The cause of circular hair loss has not been conclusively clarified. It is assumed that the body's own immune system plays a decisive role. It presumably directs its defenses not against pathogens, but against its own body. More precisely: against the hair root (follicle). This is where inflammation occurs, which disrupts hair growth and ultimately leads to hair loss.
Even though circular hair loss (alopecia areata) is rarely directly inherited, hereditary factors appear to play a role. Various genes have been identified that are or could be involved in the development of circular hair loss. For those affected, this means
-
In first-degree relatives, the risk of inheritance is between 6 and 8 percent.
-
There is no increased risk of circular hair loss in second-degree relatives: At around 1 to 2 percent, it corresponds to the risk of the population as a whole.
Circular hair loss is probably an autoimmune disease. This means that the immune system turns against its own body. Apparently, certain white blood cells (T lymphocytes) attack the roots of the hair. Although they do not destroy them, they trigger inflammatory reactions that lead to alopecia (hair loss).
It is certain that circular hair loss is not caused by malnutrition or hormones. Environmental influences do not appear to play a role either: the disease was already described in ancient times.
Circular hair loss - frequency and age
Circular hair loss affects men and women equally. All age groups can be affected, including children. However, it is young adults who suffer from circular hair loss more often than average.
Alopecia areata is not a rare disease: around 1 - 2 percent of the population receive this diagnosis in the course of their lives.
Alopecia areata symptoms
Circular hair loss typically leads to a bald spot on the scalp measuring 1-2 centimeters in diameter. Subsequently, additional areas of baldness may emerge.
While these affected patches may not always have a perfectly circular or round shape, they are visibly separated from the surrounding hair. Alopecia areata doesn't typically cause pain, though there may be a slight accompanying itch.
In the majority of those affected, there are no more than two hairless patches
However, alopecia can also spread further - to the point of complete loss of head hair or even all body hair. But there is also a way to stop alopecia areata from spreading.
Prognosis: How does circular hair loss progress?
The course of circular hair loss (alopecia areata) cannot be predicted. Some sufferers find that the alopecia disappears by itself after six to twelve months and never returns. In other patients, the lost hair also grows back, but at some point, the circular hair loss reappears. And still others experience no improvement at all, not even temporarily. Around 20-30% of those affected suffer from permanent hair loss.
Even a chronic course of circular hair loss has no effect on life expectancy.
However, alopecia areata can certainly have a negative impact on mental well-being. There are also many things to avoid when you have alopecia areata. For example, only use gentle and natural hair care products. You should also avoid stress. There are various dietary supplements that can also help you.
Alopecia areata self-care
Everyone deals with losing hair differently. Some cope well with it, for others, it is a horrific experience. Circular hair loss is easily noticeable and can make those affected feel uncomfortable.
If the hair loss occurs very suddenly or is very pronounced, it can be extremely stressful emotionally. Sometimes people are bullied and socially ostracized due to hair loss - this risk is particularly high for children and adolescents. In such cases, there are a number of things that can be done to alleviate the suffering.
Cosmetic measures
Shaving the head helps some people - many men resort to this measure.
Others prefer to wear a wig or hairpiece. Hair replacement is prescribed by a doctor.
-
If you have circular hair loss on your eyelashes, you can consider wearing artificial eyelashes.
-
If the eyebrows are affected, artificial eyebrows can be glued on, the eyebrows can be traced with make-up or tattooed (permanent make-up).
-
If the hair loss is very distressing despite cosmetic measures and is accompanied by psychological symptoms such as depression or anxiety, professional psychotherapeutic help is advisable.
Therapy: Alopecia areata treatments and alopecia areata medication
As the mechanisms behind circular hair loss are not exactly known, it cannot be cured. Nevertheless, various drugs are available to treat the symptoms. Their effect usually wears off as soon as they are discontinued.
The last words
If you suffer from alopecia areata, you are certainly not alone. However, any type of hair loss can be very distressing. That's why many people with alopecia areata and other types of hair loss seek the help and company of a support group.